CMA Inter Suggested Answers | Dec 24 Paper 9 Operations Management and Strategic Management
In this comprehensive blog, we present the CMA Intermediate Paper 9: Operations Management and Strategic Management (OMSM) question paper for the December 2024 exam, along with step-by-step suggested answers. Designed to cover key topics such as process design, capacity planning, project management, strategic analysis, and digital strategy, our solutions are fully aligned with the ICMAI study material. This blog provides exam-focused insights into both theoretical concepts and practical problem-solving techniques, helping students enhance their preparation, improve their answer-writing skills, and master high-scoring strategies. A must-read for CMA aspirants aiming to excel in the Operations Management and Strategic Management paper and achieve their professional goals.
Table of Contents
- MCQs
- 2 (a) "The Plant Layout selected
- 2 (b) What is Design Thinking?
- 3 (a) "Production Planning and
- 3 (b) METRO-WALLS ICE CREAM
- 4 (a) A project of GREEN IP Ltd
- 4 (b) Home Town Interior Decoration
- 5 (a) A computer of ROPAM Ltd
- 5 (b) BITZON Ltd., a Chemical
- 6 (a) "Objectives should possess
- 6 (b) "Big data is a collection of
- 7 (a) Identify and analyze the five
- 7 (b) "Business Environment
- 8 (a) "The Transnational Structure
- 8 (b) "The achievement of goal
- CMA Inter Dec 24 Paper 9 : Operations Management and Strategic Management detailed analysis
CMA Inter Dec 24 Suggested Answer Other Subjects Blogs :
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 5 : Business Laws and Ethics
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 6 : Financial Accounting
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 7 : Direct and Indirect Taxation
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 8 : Cost Accounting (CA)
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 10 : Corporate Accounting and Auditing
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 11 : Financial Management and Business Data Analytics
- Suggested Answer Dec 24 Paper 12 : Management Accounting
- CMA Inter Syllabus (New Updates)
CMA Inter Question Paper With Answers - OMSM Dec 2024 -
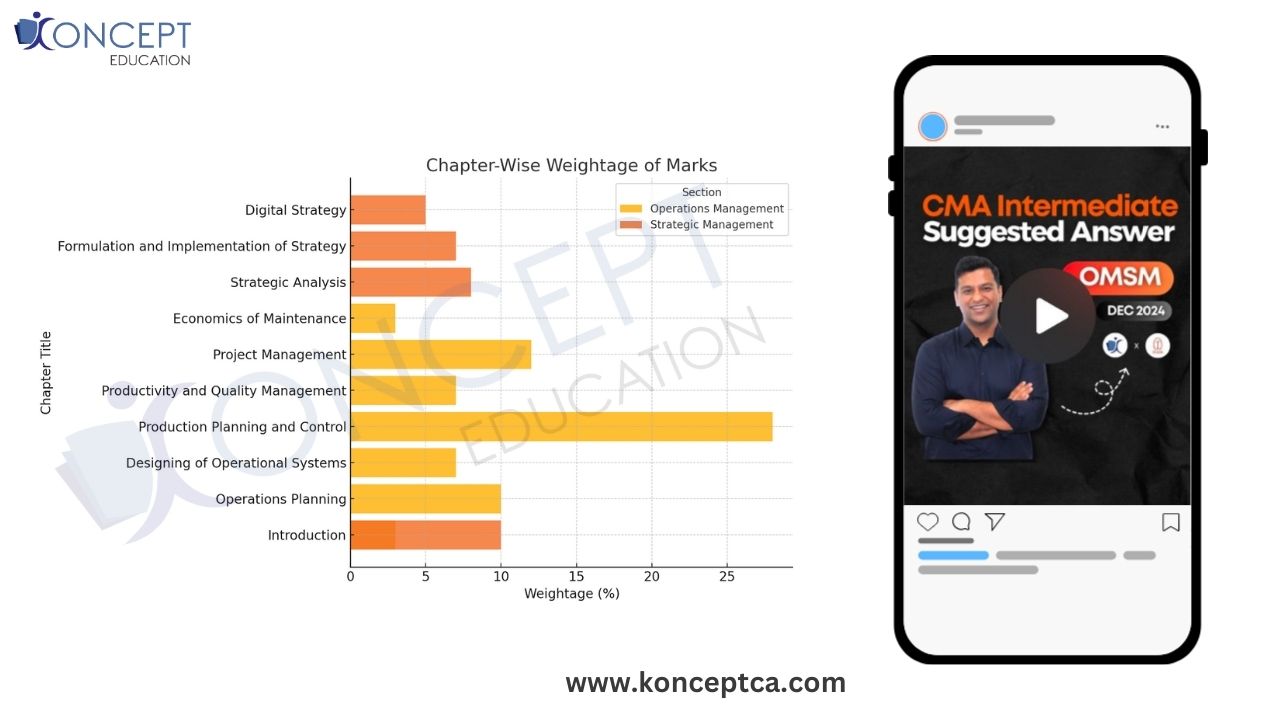
Download PDFTo further support your preparation, we’ve included an in-depth analysis of the December 2024 CMA Intermediate Operations Management and Strategic Management (OMSM) exam. This section provides valuable insights, featuring a chapter-wise marks distribution chart and a detailed breakdown of question patterns and coverage. By understanding the weightage of topics and identifying high-priority areas, this analysis empowers you to strategize your study plan effectively and maximize your scoring potential.
Section - A
MCQs
1. The ability to adapt quickly to changes in volume of demand, in the product mix demanded, and in product design or in delivery schedules, is sometimes referred to as
- Re-Engineering
- Business Process Restructuring
- Agile Manufacturing
- Right Sizing
Answer :
(C) Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing refers to the ability of an organization to respond swiftly to changes in customer demand, including volume, product mix, product design, and delivery schedules. This approach emphasizes flexibility and adaptability in manufacturing processes to gain a competitive advantage in a dynamic market environment.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 12 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
2. Which one of the following is associated with the configuration of departments, work centres and equipment and machinery, with focus on the flow of materials or work through the production system?
- Facility Location
- Facility Layout
- Capacity Planning
- Process Design
Answer :
(b) Facility Layout
Facility layout refers to the configuration of departments, work centers, and equipment and machinery with a focus on the flow of materials or work through the production system. It aims to optimize the arrangement of resources and operations to improve efficiency and workflow.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 47 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
3. In which one of the following phases of the product life cycle, organisations get engaged in aggressive promotional and pricing program?
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
Answer :
(c) Maturity
In the maturity phase of the product life cycle, organizations typically engage in aggressive promotional and pricing programs to sustain their position in a saturated market. This phase focuses on differentiation and maintaining market share while slowing the progression toward the decline phase.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 94 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
4. The Annual Carrying cost of Material ZB is 3.60 per unit and its Total Carrying cost is 9,000 per annum. If there is no safety stock of Material 1B, what will be the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) for Material ZB?
- 5000 units
- 6000 units
- 6500 units
- 4000 units
Answer :
(A) 5000 units
Total Carrying Cost = ( Order Quantity / 2 ) * CC pu pa
9000 = ( Q / 2 ) * 3.6
Hence Q = 5000 units
5. ZOOS Ltd., a manufacturing firm, has four Work Centres A, B, C & D in series with individual capacities in units per day shown in the figure below:
|
Work Centers
|
|
Raw materials
|
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
Actual output
|
|
380
|
360
|
340
|
400
|
300
|
What is the system Efficiency?
- 75.25%
- 80.3%
- 99%
- 88.23%
Answer :
(D) 88.23%
The bottle neck centre is the work centre having the minimum capacity. Hence, work centre C is the bottleneck centre.
System capacity is the maximum units that are possible to produce in the system as a whole. Hence, system capacity is the capacity of the bottle neck centre i.e., 340 units.
System efficiency = ( Actual output / System Capacity) = 300 / 340 × 100 (i.e., maximum possible output) = 88.23%
(ICMAI Study Material Page 38 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
6. A cement factory of SITON (C) Ltd., in Madhya Pradesh works 7 days a week in 3 shifts per day having maintenance in the first shift of around 2 hours. It has roughly 100 workers which produces only pozzolanic properties cement better known as PPC. The output per month is around 2500 tonnes of PPC. What will be productivity per worker?
- 20 tonnes
- 30 tonnes
- 25 tonnes
- 15 tonnes
Answer :
(C) 25 tonnes
Productivity per worker = 2500/100 = 25 tonnes
(ICMAI Study Material Page 275 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
7. For Quality Assurance in the Design, Production, Installation and Servicing the ___________Model is used.
- ISO 9002
- ISO 9001
- ISO 9003
- None of the above options
Answer :
(B) ISO 9001
ISO 9001 is specifically used as the model for Quality Assurance in Design, Production, Installation, and Servicing. It ensures that the processes involved in these stages meet customer requirements and comply with standards.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 270 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
8. This _______provides the broad ''DATA", from which to identify key drivers of change.
- SWOT Analysis
- BCG Matrix
- PESTEL Analysis
- Critical Success Factors
Answer :
(C) PESTEL Analysis
The PESTEL analysis provides the broad "data" needed to identify key drivers of change. It categorizes environmental influences into Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors, which are critical for understanding the external environment of an organization.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 428 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
9. Which one of the following cannot be closely associated with the "Red Ocean Strategy"?
- Boat the Competition
- Make the Value Cost trade-off
- Make the Competition irrelevant
- Exploit Existing Demand
Answer :
(C) Make the Competition Irrelevant
"Red Ocean Strategy" focuses on competing in existing markets by outperforming rivals, exploiting existing demand, and making the value-cost trade-off. The concept of "making the competition irrelevant" is a characteristic of "Blue Ocean Strategy," not Red Ocean Strategy.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 393 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
10. The process of______ requires co-ordination across the entire organisation and involves business culture changes.
- Digital Strategy
- Digitization
- Digital Transformation
- Data Aggregation
Answer :
(C) Digital Transformation
Digital transformation involves changes in customer experience, operational processes, and business models. It requires coordination across the entire organization and necessitates changes in business culture to adapt to the digital landscape.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 499 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
11. Forecasting the weather is an example of_____
- Narrow Al
- General Al/Human-Level
- Super Al
- Deep-Learning
Answer :
(A) Narrow AI
Forecasting the weather is an example of Narrow AI, which is designed to perform specific tasks effectively, such as making predictions or automating processes in a defined area. Unlike General AI, Narrow AI focuses on specialized functions and is not equipped to handle broader, human-level intelligence tasks
(ICMAI Study Material Page 510 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
12. Which type of Production Control is most prominently applied in the industries like textiles, and book & magazine printing industries?
- Batch Control
- Load Control
- Order Control
- Block Control
Answer :
(d) Block Control
Block control is prominently applied in industries like textiles and book/magazine printing. It ensures items remain separated, which is a fundamental requirement in these industries.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 116 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
13. The Work Breakdown Structure is typically developed in which one of the following phases of the project management life cycle?
- Project Initiation Phase
- Project Planning Phase
- Project Quality Management Phase
- Execution Phase
Answer :
(b) Project Planning Phase
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is typically developed during the Project Planning Phase of the project management life cycle. This phase includes defining the scope, creating detailed plans, and establishing the WBS to ensure the project's deliverables and tasks are well-organized.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 290 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
14. Strategy Formulation is characterised by—
- The focus is on effectiveness.
- It requires motivation and leadership skills.
- It involves managing forces during action.
- It is primarily an operational process
Answer :
(a) The focus is on effectiveness.
Strategy formulation is characterized by activities that focus on effectiveness, involving high-level planning to position forces before action. It is an intellectual process requiring analytical skills, and it precedes strategy implementation, which focuses on efficiency.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 477 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
15. Which one of the following activities involves receiving, storing and distributing inputs to the production process?
- Inbound Logistics
- Operations
- Marketing & Sales
- Outbound Logistics
Answer :
(a) Inbound Logistics
Inbound logistics includes activities such as receiving, storing, and distributing inputs to the production process. This is a critical primary activity in the value chain, which ensures materials and resources are available for the operations phase.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 434 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Section - B
Question - 2 (a)
"The Plant Layout selected in conformity with Layout Principles should be an ideal one"— In this context, align those Plant Layout Principles.
Answer :
Plant Layout Principles
Plant layout involves the arrangement of physical facilities such as machinery, equipment, and workspace to optimize workflow and efficiency. For an ideal layout, certain principles must be adhered to. These principles ensure smooth production processes, cost-effectiveness, and employee satisfaction.
1. Principle of Minimum Movement
- Explanation: Materials, tools, and workers should have the shortest possible travel distance within the plant to minimize unnecessary movement and associated costs.
- Example: Positioning machines close to related workstations to reduce material handling.
2. Principle of Flow
- Explanation: The layout should ensure a smooth and uninterrupted flow of materials, information, and work through the production process.
- Example: Designing assembly lines to follow a logical sequence of operations.
3. Principle of Space Utilization
- Explanation: Efficient utilization of available space is crucial. Both horizontal and vertical space should be utilized optimally.
- Example: Installing mezzanine floors or arranging equipment vertically when floor space is limited.
4. Principle of Safety and Comfort
- Explanation: The layout should ensure worker safety and comfort to reduce accidents and increase productivity.
- Example: Providing ample workspace, proper lighting, and ventilation.
5. Principle of Flexibility
- Explanation: The layout should be adaptable to changes in product design, production volume, and technology.
- Example: Modular layouts that allow easy reconfiguration for new processes.
6. Principle of Accessibility
- Explanation: Machines, equipment, and materials should be easily accessible for maintenance, repair, and operations.
- Example: Allocating space around machines to allow easy access during breakdowns.
7. Principle of Integration
- Explanation: The layout should integrate all components of production into a cohesive system to achieve efficiency.
- Example: Linking manufacturing, storage, and dispatch areas in a streamlined manner.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 41 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 2 (b)
What is Design Thinking? Briefly discuss the five stages of Design Thinking.
Answer :
Design Thinking is a human-centered, iterative approach to problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and rationality to address user needs. It is widely used in innovation, business, and product development to create solutions that are desirable, feasible, and viable.
Design Thinking helps in understanding the problem deeply, generating innovative ideas, and testing solutions effectively. It is not linear and often involves iterative back-and-forth between stages.
Five Stages of Design Thinking
1. Empathize
- Purpose: Gain a deep understanding of the users and their needs.
- Activities: Conduct interviews, surveys, and observations to understand users' emotions, experiences, and challenges.
- Example: A team designing a mobile app might interview users about their app preferences and frustrations.
2. Define
- Purpose: Synthesize information gathered in the Empathize phase to articulate the problem clearly.
- Activities: Develop a problem statement or a user-centered need statement.
- Example: “Users need a faster and more secure way to make online payments.”
3. Ideate
- Purpose: Generate a wide range of creative solutions to the problem.
- Activities: Brainstorming, sketching, and using techniques like mind mapping to explore innovative ideas.
- Example: For the payment app, ideas might include one-click payment or biometric authentication.
4. Prototype
- Purpose: Create simplified versions of the potential solutions for testing.
- Activities: Develop mockups, wireframes, or physical models to bring ideas to life.
- Example: A prototype for the app might include a clickable demo showing the payment process.
5. Test
- Purpose: Validate the prototype by gathering feedback from users.
- Activities: Conduct usability testing, observe user interactions, and refine the solution.
- Example: Users test the app prototype, and feedback leads to adding a clearer navigation menu.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 99 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 3 (a)
"Production Planning and Control fulfils its various objectives by focusing on the several important points/issues". With reference to this statement, append those said important points/issues.(Any Ten)
Answer :
View solution in koncept education app - Download App
Question 3 (b)
METRO-WALLS ICE CREAM PARLOUR observed that during summer months the daily sales of its ice cream depends on the average day temperature as shown in the following Table:
|
Average Day Temperature in Centigrade(X)
|
20
|
25
|
30
|
35
|
40
|
|
Daily Sale of Ice Cream(in Thousand ₹)
|
10
|
20
|
30
|
40
|
50
|
Required:
(i) Fit a linear regression of Y on X,
(ii) Estimate the trend values of daily sales of ice cream for average day temperatures of 32 and 42 centigrade.
(iii) Estimate the Average Day Temperature (in Centigrade) for the daily sale Of ice cream of ₹ 60 thousand
Answer :
Linear Regression Analysis
(i) Fit a Linear Regression of Y on X
The equation of a linear regression line is:
Y = a + bX
Where:
- b = (n∑XY − ∑X∑Y) / (n∑X² − (∑X)²)
- a = (∑Y / n) − b(∑X / n)
Step 1: Compute Required Values
Given the data:
| X (Average Day Temperature) |
Y (Daily Sales in ₹ Thousand) |
XY |
X² |
| 20 |
10 |
200 |
400 |
| 25 |
20 |
500 |
625 |
| 30 |
30 |
900 |
900 |
| 35 |
40 |
1400 |
1225 |
| 40 |
50 |
2000 |
1600 |
| Total |
150 |
5000 |
4750 |
n = 5, ∑X = 150, ∑Y = 150, ∑XY = 5000, ∑X² = 4750
Step 2: Calculate Slope (b)
b = (5(5000) − (150)(150)) / (5(4750) − (150)²)
b = (25000 − 22500) / (23750 − 22500) = 2500 / 1250 = 2
Step 3: Calculate Intercept (a)
a = (∑Y / n) − b(∑X / n)
a = (150 / 5) − 2(150 / 5)
a = 30 − 60 = −30
Regression Line:
Y = −30 + 2X
(ii) Estimate Daily Sales for X = 32°C and X = 42°C
- For X = 32°C: Y = −30 + 2(32) = 34 ₹ Thousand
- For X = 42°C: Y = −30 + 2(42) = 54 ₹ Thousand
(iii) Estimate X for Y = ₹ 60 Thousand
Rearranging the regression equation:
60 = −30 + 2X
2X = 90 ⇒ X = 45°C
Final Answers:
- Regression Line: Y = −30 + 2X
- Daily Sales at 32°C: ₹ 34 Thousand; at 42°C: ₹ 54 Thousand
- Average Day Temperature for ₹ 60 Thousand Sales: 45°C
Question 4 (a)
A project of GREEN IP Ltd., consists of four major jobs, for which four contractors have submitted tenders. The tender amounts, in thousands of rupees, are given below:
|
Contractors
|
JOBS
|
|
|
|
| |
A
|
B
|
C
|
D
|
|
1
|
39
|
70
|
37
|
50
|
|
2
|
20
|
27
|
47
|
63
|
|
3
|
25
|
37
|
58
|
49
|
|
4
|
43
|
48
|
46
|
50
|
(Each Contractor has to be assigned only one Job)
Required:
(i) Analyze and assign the Jobs to appropriate Contractors so as to minimize the Total Cost of the Project.
(ii) Assess the Total Costs of the Project.
Answer :
Solution: Job Assignment Problem
Given Cost Matrix
| Contractors \ Jobs |
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1 |
39 |
70 |
37 |
50 |
| 2 |
20 |
27 |
47 |
63 |
| 3 |
25 |
37 |
58 |
49 |
| 4 |
43 |
48 |
46 |
50 |
(i) Analyze and Assign Jobs Using the Hungarian Method
Step 1: Row Reduction
Subtract the smallest value in each row from every element in that row:
| Contractors \ Jobs |
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1 |
2 |
33 |
0 |
13 |
| 2 |
0 |
7 |
27 |
43 |
| 3 |
0 |
12 |
33 |
24 |
| 4 |
0 |
5 |
3 |
7 |
Step 2: Column Reduction
Subtract the smallest value in each column from every element in that column:
| Contractors \ Jobs |
A |
B |
C |
D |
| 1 |
2 |
28 |
0 |
6 |
| 2 |
0 |
2 |
27 |
36 |
| 3 |
0 |
7 |
33 |
17 |
| 4 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
Step 3: Optimal Assignment
Using the reduced matrix, we assign jobs to minimize costs:
- Job A → Contractor 3 (Cost = ₹ 25,000)
- Job B → Contractor 2 (Cost = ₹ 27,000)
- Job C → Contractor 1 (Cost = ₹ 37,000)
- Job D → Contractor 4 (Cost = ₹ 50,000)
(ii) Assess the Total Cost of the Project
The total cost is the sum of the costs for the assigned jobs:
Total Cost = 25,000 + 27,000 + 37,000 + 50,000 = ₹ 1,39,000
Final Answer:
- Job Assignments:
- Job A → Contractor 3
- Job B → Contractor 2
- Job C → Contractor 1
- Job D → Contractor 4
- Total Cost of the Project: ₹ 1,39,000
Question 4 (b)
Home Town Interior Decoration Ltd., uses a costly drier while painting the fire protection doors. The drier is highly volatile. It cannot be stored. In order to meet the requirement of drier, the exact quantity is purchased every day and consumed. The Management of the Company wants to Simulate the demand of the drier. For this the Management of the Company collected data for past 100 days for the application of the drier on the number of doors and the same data are shown in the table below:
|
Daily Demand (No.driers)
|
Number of Days
|
|
0
|
20
|
|
1
|
30
|
|
2
|
20
|
|
3
|
10
|
|
4
|
6
|
|
5
|
4
|
|
6
|
10
|
Consider the following Table of two Digit Random Numbers:
|
Random Numbers
|
03
|
23
|
36
|
93
|
69
|
43
|
87
|
51
|
11
|
08
|
Required:
(i) Using the following generated random numbers in Sequence. generate the demand of driers for next ten days.
(ii) Assess the average demand of drier per day.
Answer :
View solution in koncept education app - Download App
Question 5 (a)
A computer of ROPAM Ltd., has 1000 nos. of Electronic Tubes. They are subject to Mortality as given below:
|
Period
|
Age at failure
|
Probability of Failure
|
|
1
|
0 -200
|
0.10
|
|
2
|
201 - 400
|
0.26
|
|
3
|
401 - 600
|
0.35
|
|
4
|
601 - 800
|
0.22
|
|
5
|
801 - 1000
|
0.07
|
If the tubes are group replaced, the cost of replacement is 150 per Electronic tube. Group replacement can be done at fixed intervals in the night shift when the computer is not normally used. Replacement of individual Electronic tubes which fail in Service Cost 600 per Electronic tube.
Assume that:
(1) Eiectromc Tubes that fail during a period are replaced just before the end of the period,
(2) The actual percentage of failure during a period a sub - population of the tubes with the same age is the same as the expected percentages of failure the period for the sub - population.
Required:
(i) Analyze the number of Electronic Tubes to be replaced every period.
(ii) Assess the failure costs(₹) on average of individual replacement of electronic tubes.
(iii) Identify at what interval of time the Company should replace all the electronic Tubes.
(iv) Advice which policy of replacement will be economical to the Company.
Answer :
View solution in koncept education app - Download App
Question 5 (b)
BITZON Ltd., a Chemical Product Manufacturing Company have split their Schedule of Implementation into the following 6 activities and have estimated Time Duration (in weeks) under 3 Scenarios as under:—
|
Activity and Identification
|
Optimistic time estimate (in Weeks)
|
Pessimistic time estimate (in Weeks)
|
Most likely time estimate (in Weeks)
|
|
A (1 – 2)
|
5
|
11
|
8
|
|
B (1 – 3)
|
18
|
26
|
22
|
|
C (2 – 4)
|
15
|
25
|
20
|
|
D (3 – 4)
|
4
|
12
|
8
|
|
E (4 – 5)
|
8
|
12
|
10
|
|
F (3 – 5)
|
14
|
26
|
20
|
Required:
(i) Assess the expected duration (in weeks) for each activity.
(ii) Design the PERT Network Diagram and indicate all paths through it.
(iii) Identify the Critical Path and its Duration (in weeks).
(iv) Analyze and indicate the Total Float and Free Float available on each activity.
Answer :
View solution in koncept education app - Download App
Question 6 (a)
"Objectives should possess certain desirable characteristics in order to be effective". In this context, identify and explain those characteristics of Effective Objectives.
Answer :
Objectives are essential for guiding an organization's activities and evaluating its performance. To be effective, objectives must possess specific desirable characteristics. These characteristics ensure that the objectives are actionable, measurable, and aligned with organizational goals.
1. Specific
- Explanation: Objectives should clearly state what is to be achieved without ambiguity.
- Example: Instead of saying "increase sales," an objective should specify "increase sales by 10% in the next quarter."
2. Measurable
- Explanation: Objectives must be quantifiable to track progress and evaluate success.
- Example: Use numerical targets such as "reduce production waste by 15%."
3. Achievable
- Explanation: Objectives should be realistic and attainable given the available resources and constraints.
- Example: Setting a target to "double revenue in a month" may not be achievable for most organizations.
4. Relevant
- Explanation: Objectives should align with the overall mission, vision, and strategic goals of the organization.
- Example: A company's objective to "enhance employee training programs" aligns with the broader goal of improving operational efficiency.
5. Time-Bound
- Explanation: Objectives should have a clearly defined timeline to create a sense of urgency and accountability.
- Example: "Complete the product launch by December 2024.
6. Challenging
- Explanation: Effective objectives should push the organization to improve and achieve higher levels of performance.
- Example: "Expand market share by 20% in a competitive industry."
7. Communicable
- Explanation: Objectives should be easily understood by all stakeholders to ensure alignment and effective collaboration.
- Example: Using simple, direct language to state objectives, such as "reduce customer complaints by 30%."
8. Flexible
- Explanation: Objectives should be adaptable to changes in the internal or external environment.
- Example: Revising objectives in response to new market trends or unforeseen challenges.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 400 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 6 (b)
"Big data is a collection of data that is huge in volume and growing exponentially with time". In this Context Identify the different types of big data and briefly explain the main characteristics of big data.
Answer :
Types of Big Data
Big data can be broadly categorized into three types:
- Structured Data:
- Definition: Data that is organized in a defined format such as rows and columns, making it easy to store, process, and retrieve using databases.
- Examples: Transaction records, customer databases, and sensor data.
- Unstructured Data:
- Definition: Data that does not follow a predefined model or structure, making it more complex to process and analyze.
- Examples: Images, videos, social media posts, and emails.
- Semi-Structured Data:
- Definition: Data that does not follow a strict structure but contains tags or markers to separate elements, offering some level of organization.
- Examples: XML files, JSON data, and web logs
Characteristics of Big Data (The 5 V's)
- Volume:
- Definition: Refers to the massive amount of data generated every second. This characteristic is the defining trait of big data.
- Example: Data generated by social media platforms, IoT devices, and e-commerce sites.
- Velocity:
- Definition: Describes the speed at which data is generated and processed to meet real-time requirements.
- Example: Real-time traffic data, stock market feeds, and streaming platforms.
- Variety:
- Definition: Indicates the diverse types and sources of data, such as structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data.
- Example: Combining social media data, transactional data, and video content for analysis.
- Veracity:
- Definition: Refers to the reliability and accuracy of the data. It deals with issues like inconsistencies, biases, and inaccuracies in data.
- Example: Filtering out fake news from real news in a dataset.
- Value:
- Definition: Focuses on extracting meaningful insights and actionable knowledge from the data to drive decision-making.
- Example: Predicting customer behavior to tailor marketing campaigns.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 506 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 7 (a)
Identify and analyze the five main steps involved in the Formal Strategic Planning Process.
Answer :
Five Main Steps in the Formal Strategic Planning Process
1. Establishing Vision, Mission, and Objectives
- Description: This step involves clarifying the organization’s purpose (mission), long-term aspirations (vision), and specific goals (objectives). It sets the direction for all strategic efforts.
- Key Activities:
- Define the organization's mission and vision statements.
- Set measurable, achievable, and time-bound objectives.
2. Environmental Analysis
- Description: This step focuses on analyzing external and internal environments to identify opportunities, threats, strengths, and weaknesses (SWOT analysis).
- Key Activities:
- External analysis: Using tools like PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal).
- Internal analysis: Assessing resources, capabilities, and value chains.
3. Strategy Formulation
- Description: In this step, the organization develops strategies based on the insights gained from environmental analysis to achieve its objectives.
- Key Activities:
- Decide on corporate-level strategies (e.g., diversification or consolidation).
- Develop business-level strategies (e.g., cost leadership, differentiation).
4. Strategy Implementation
- Description: This step involves putting the formulated strategies into action through effective allocation of resources and alignment of processes.
- Key Activities:
- Design organizational structures and workflows.
- Communicate strategies to all stakeholders.
- Allocate budgets and assign responsibilities.
5. Evaluation and Control
- Description: The final step ensures that strategies are on track to achieve objectives through continuous monitoring and adjustment.
- Key Activities:
- Measure performance using key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Compare actual outcomes with planned objectives.
- Make adjustments to strategies or implementation plans as needed.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 447 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 7 (b)
"Business Environment exhibits many characteristics". In this event, demonstrate in brief the said important characteristics of the Business Environment.
Answer :
The business environment exhibits several important characteristics that define its complexity and dynamics:
- Complexity:
- The business environment comprises various interrelated factors, such as economic, social, political, technological, and legal conditions. These factors interact with one another to create a network of influences that can be challenging to understand as a whole.
- Dynamic Nature:
- It is constantly changing due to the impact of various forces such as technological advancements, market trends, regulatory changes, and globalization. These changes can significantly alter the structure and functioning of industries.
- Multifaceted:
- Changes in the business environment are perceived differently by different organizations and individuals. What might be an opportunity for one entity could pose a threat to another, depending on their circumstances and preparedness.
- Far-Reaching Impact:
- The business environment has a significant impact on organizations, affecting their strategies, operations, and overall success. It influences decision-making processes and can determine the long-term survival and growth of an organization.
These characteristics highlight the need for organizations to continuously analyze and adapt to their external environment to remain competitive and sustainable.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 429 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 8 (a)
"The Transnational Structure seeks to obtain the best form of the two extreme International Strategies, the Multi Domestic Strategy and the Global Strategy", In this context, identify and discuss the characteristics of Transnational Structure.
Answer :
he Transnational Structure aims to combine the benefits of Global Strategy (global efficiency and integration) and Multi-Domestic Strategy (local responsiveness and flexibility). It is characterized by the following:
1. Global Integration with Local Responsiveness:
- Transnational companies balance the need for efficiency across global operations with the flexibility to adapt to local market conditions.
- They standardize certain operations to achieve economies of scale while customizing others to meet local needs.
2. Network Structure:
- Instead of centralized or decentralized control, transnational firms operate through a network of semi-autonomous subsidiaries.
- Decision-making authority is distributed, and units collaborate to share knowledge and best practices.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability:
- The transnational structure allows firms to respond quickly to changes in the global market while maintaining a local presence to address specific regional demands.
- This structure supports innovation by encouraging interaction among global and local teams.
4. Knowledge Sharing and Coordination:
- Knowledge flows freely between headquarters and subsidiaries, as well as among subsidiaries themselves, creating a learning organization.
- This horizontal flow of information helps the organization leverage global insights while catering to local preferences.
5. Dual Pressures:
- The transnational model inherently deals with the dual pressures of globalization and localization, making it complex and challenging to manage.
- It requires a robust system of communication and coordination to balance competing demands.
6. Cultural Sensitivity:
- Success in a transnational structure depends on understanding and integrating diverse cultural, political, and social norms across regions.
Example of a Transnational Company:
- Companies like Unilever and Nestlé exemplify transnational structures. They centralize functions like R&D for global efficiency while allowing local subsidiaries to adapt marketing strategies to fit local tastes and preferences.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 472 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Question 8 (b)
"The achievement of goal congruence is essential in order to increase the profitability of the organization and to achieve its goals". With reference to this statement, demonstrate some of the areas that have the ability to create goal congruence.
Answer :
Communication and Understanding:
- Clear communication of organizational goals ensures that employees understand the desired actions and objectives.
- Both formal channels (e.g., financial documents, budgets) and informal methods (e.g., meetings, one-on-one interactions) are utilized.
- Proper internalization of goals reduces misunderstandings and helps employees feel confident in achieving them.
Creating Direction:
- A lack of guidance can lead to misalignment of employee efforts. By establishing clear performance management systems, employees are informed about expectations.
- Understanding strategic objectives and value drivers ensures employees focus their efforts effectively.
Motivation:
- Motivation plays a crucial role in ensuring that employees align their self-interests with organizational goals.
- Varied factors influence motivation: recognition, appraisals, and a sense of responsibility. Greater employee motivation typically leads to stronger alignment.
Incentives:
- Providing rewards such as bonuses or share-based incentives encourages employees to achieve organizational objectives.
- Properly structured incentives align personal goals with those of the organization, fostering increased effort and productivity.
Connecting Performance Measures and Incentives:
- Creating a direct link between performance metrics and rewards ensures alignment.
- Employees are more likely to focus on critical objectives when their achievements are tied to measurable outcomes and rewards.
(ICMAI Study Material Page 492 | This Questions is also a part of Konceptca.com Question Library)
Operations Management and Strategic Management detailed analysis
To further support your preparation, we’ve included an in-depth analysis of the December 2024 CMA Intermediate Operations Management and Strategic Management (OMSM) exam. This section provides valuable insights, featuring a chapter-wise marks distribution chart and a detailed breakdown of question patterns and coverage. By understanding the weightage of topics and identifying high-priority areas, this analysis empowers you to strategize your study plan effectively and maximize your scoring potential.




