
CA Foundation Law paper Jan 2025 with answers
Looking for solutions to the CA Foundation Law Paper January 2025 with Answers? You’re in the right place! This blog covers everything you need to know about the CA Foundation January 2025 Exam, including detailed solutions and insights to help you excel. We’re here to provide a comprehensive breakdown of the January 2025 Law Paper
Table of Contents
CA Foundation Jan 25 Suggested Answer Other Subjects Blogs :
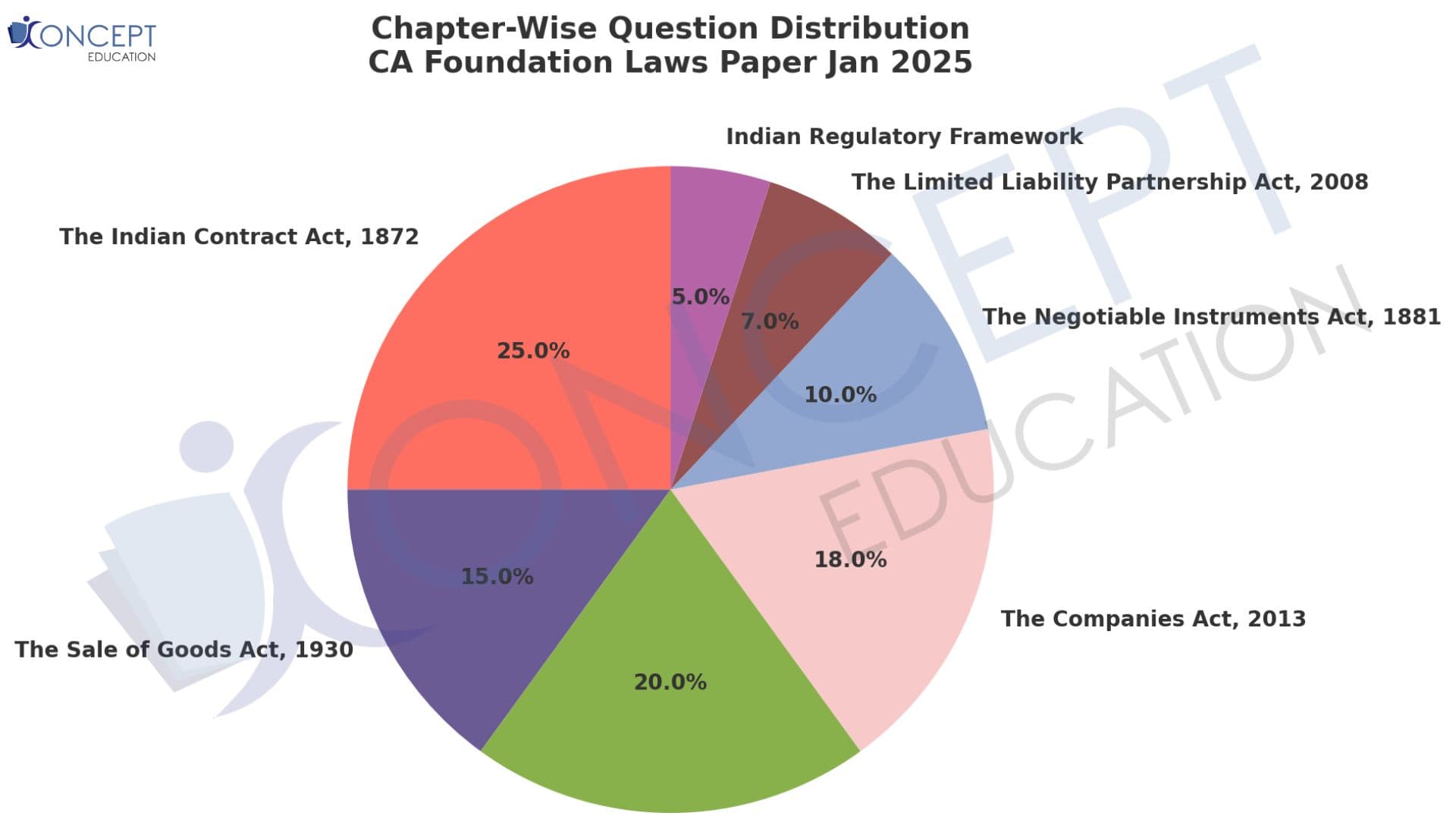
CA Foundation LAW Paper Jan 25 Analysis
The Jan 25 CA Foundation Laws paper presented a balanced mix of easy, medium, and hard questions. Approximately 35-40% of the paper consisted of easy questions focusing on definitions and basic provisions, such as partnership terms and simple contract principles. Around 45-50% of the questions were of medium difficulty, involving case-based scenarios that required the application of concepts, like minor rights in a partnership or breaches under the Sale of Goods Act. The remaining 15-20% were hard, featuring complex scenarios that demanded an in-depth understanding, such as entrenchment provisions or disputes related to negotiable instruments. To excel, students should focus on mastering the fundamentals, practicing case-based questions, and understanding how legal provisions apply to real-life situations.
Q 1 (A) :
Examine the validity of the following agreements under the provisions of The Indian Contract Act, 1872 and justify your answer:
Answer:
1. Mrs. Priya pays ₹10,000 to a marriage bureau for providing information about prospective grooms
Relevant Provisions
Marriage brokerage agreements: An agreement to negotiate marriage for reward, which is known as a marriage brokerage contract, is void, as it is opposed to public policy. For instance, an agreement to pay money to a person hired to procure a wife
is opposed to public policy and therefore void.
Note: Marriage bureau only provides information and doesn’t negotiate marriage for reward, therefore, it is not covered under this point.
Conclusion
This agreement is valid under the Indian Contract Act, 1872 because it fulfills all the essentials of a valid contract and does not fall under any prohibited category.
2. Bharat agrees to sell his white bull to John, but unknown to both, the bull was already dead
Relevant Provisions
Section 20 of the Act states that if both parties are under a mistake as to a matter of fact essential to the agreement, the agreement is void.
Analysis
Conclusion
This agreement is void under Section 20 of the Indian Contract Act, as there is a mutual mistake regarding the existence of the subject matter.
3. Rishabh sells the goodwill of his shop to Omkar for ₹10,00,000 and promises not to carry on a similar business within the local limits for as long as Omkar carries on a like business
Relevant Provisions
An agreement by which any person is restrained from exercising a lawful profession, trade or business of any kind, is to that extent void. But this rule is subject to the following exceptions, namely, where a person sells the goodwill of a business and agrees with the buyer to refrain from carrying on a similar business, within specified local limits, so long as the buyer or his successor in interest carries on a like business therein, such an agreement is valid (goodwill is the advantage enjoyed by a business on account of public patronage and
encouragement from habitual customers). The local limits within which the seller of the goodwill agrees not to carry on similar business must be reasonable.
Conclusion
This agreement, being a reasonable restraint in connection with the sale of goodwill, falls under the statutory exception to Section 27. It is therefore valid
4. A property worth ₹2,00,000 was agreed to be sold for ₹25,000 by a person of unsound mind
Relevant Provisions
Section 11 of the Act: A person is competent to contract if (a) he is of the age of majority, (b) is of sound mind, and (c) is not disqualified from contracting by any law to which he is subject.
Analysis
Conclusion
Since one of the essential elements (capacity to contract) is absent, the agreement is void.
Q 1 (B) : (i)
“Harmony Foundation” is a newly incorporated company focused on promoting education and healthcare services in rural areas. The company is registered as a section 8 company with a clear plan to reinvest all profits into its activities, and a license has been accorded by the Central Government. For the financial year ending on 31st March, 2024, the company earned a substantial profit and transferred some amount to M/S LMP Associates (a Partnership firm and one of the members of the Harmony Foundation). Subsequently, on the complaint of one of the members, the Central Government, after giving an opportunity of being heard, directed the company to be wound up on the ground that a partnership firm cannot be a member of the section 8 company and it cannot transfer any part of profit to the firm. Explain, in the light of the provisions of The Companies Act, 2013, whether the ground taken for winding up is sufficient.
Answer: There are 2 issues that need disscussion
Issue 1 : Can partnership firm be a member of the section 8 company ?
There is no prohibition under the Companies Act, 2013 that disqualifies a partnership firm from holding shares or being a member of a Section 8 company. Hence A partnership firm can be a member of Section 8 company.
Issue 2 : Section 8 company cannot transfer any part of profit to the firm ?
Section 8(1) of the Act requires that the company:
It follows that any direct or indirect distribution of profits as dividends to members would breach the Section 8 license conditions. However, not all payments made to a member are necessarily “distribution of profits.” Examples include:
Under Section 8(6) and (7), the Central Government can revoke a Section 8 company’s license if:
Upon revocation, the Central Government may, in the public interest, either:
Conclusion
The sole ground cited in the problem is:
However, as explained above:
Hence, merely citing the membership of a partnership firm and a transfer of funds to it does not ipso facto establish that the Section 8 company has violated its license conditions or that it should be wound up.
Q 1 (B) : (ii)
Justice Private Limited has 9 directors on its Board of Directors. The company’s Articles of Association currently state that the quorum for board meetings shall be 1/3rd of the total strength or 2 directors, whichever is higher. The company now intends to amend this article to specify that the quorum for board meetings shall be 1/3rd of the total strength or 4 directors, whichever is higher. Advise the company on the procedure for including this entrenchment provision in its Articles, in accordance with the provisions of The Companies Act, 2013. Would your advice differ if the company were a public company?
Answer:
Under Section 5(4) of the Companies Act, 2013, to introduce an entrenchment provision (i.e., making any alteration in the Articles more stringent), a private company must obtain unanimous written consent of all its members, whereas a public company must pass a special resolution (75% majority). After approval, the company must file the altered Articles with the Registrar of Companies (RoC) within 30 days.
In this scenario (Justice Private Limited), the higher quorum requirement would be treated as an entrenchment provision; hence, unanimous consent of all shareholders is required before filing the amendment with the RoC. If it were a public company, a special resolution at a general meeting would suffice instead of unanimous consent.
Q 1 (C) :
A minor admitted to the benefits of a partnership firm is entitled to certain rights and may also have liabilities to third parties for the acts of the firm. Discuss the rights and liabilities (before attaining majority only) of the minor under The Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
Answer:
Q 2 (A) : (i)
MNO Limited, a supplier of electronic components, entered into a contract on August 1, 2023, with PQR Enterprises for the sale of 1000 units of microchips. The contract specifically identified the microchips by serial numbers and confirmed that they were in a deliverable state, stored in MNO Limited’s warehouse. The contract stipulated that the goods would be delivered on September 1, 2023.
On August 10, 2023, a flood occurred, damaged the warehouse, and destroyed the entire stock of microchips, including the 1000 units intended for PQR Enterprises. Examine, with reference to the provisions of The Sale of Goods Act, 1930, who shall suffer the loss? What will be your answer if the microchips are not specifically identified and marked for PQR Enterprises at the time of the contract?
Answer:
Q 2 (A) : (ii)
A purchases a motorcycle from B and uses it for some time. It turns out that the motorcycle sold by B to A was a stolen one and had to be returned to a rightful owner. A brings action against B for the return of the price. Will he succeed? Examine this with reference to the provisions of The Sale of Goods Act, 1930.
Answer:
Q 2 (B) :
Write in brief the content and model of the Articles of Association (AOA), according to which the director and other officers are required to perform their functions as regards the management of the company, its accounts, and audit.
Answer:
Q 2 (C) :
Dyana and Bharti, newly qualified chartered accountants, wish to form a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) to provide their professional services. They seek information about the provisions of The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, specifically regarding the incorporation document. Additionally, they want to know whether the statement filed along with the incorporation document serves as sufficient evidence that all legal requirements for the incorporation of the LLP have been fulfilled. Explain these aspects to them.
Answer:
Q 3 (A) :
P, Q, and R, are partners in a construction firm, PQR Associates. P buys cement on behalf of the firm from D. The cement is used in the ordinary course of the firm’s business. P uses the cement for his personal purposes. The supplier D, who is unaware of the private use of cement by P, claims the price from the firm. The firm refuses to pay for the price, on the ground that the cement was never received by it. Referring to the provisions of The Indian Partnership Act, 1932, answer the following:
Answer:
Q 3 (B) : (i)
The extract of the major shareholders holding paid-up share capital in Rural Development Fin. Corp. Ltd., are as follows:
Whether the company would be considered as a Public Financial Institution (PFI) under the provisions of The Companies Act, 2013? Explain in brief about various institutions regarded as ‘Public Financial Institutions’ under The Companies Act, 2013.
Answer:
Q 3 (B) : (ii)
Whether it is mandatory to have a common seal for the company? If not, then what are the other options available as per The Companies Act, 2013?
Answer:
Q 3 (C) :
What are the agreements which are held to be opposed to public policy under The Indian Contract Act, 1872? Explain any 6 such agreements.
Answer:
Q 4 (A) :
A, B, and C jointly promised to pay D a sum of ₹6,000. Examine, considering the provisions of The Indian Contract Act, 1872 –
(i) Can D compel any of the three parties A, B, and C to pay him ₹6,000?
(ii) C is compelled to pay the whole of the amount to D. Can he recover anything from A and B, when –
Answer:
Q 4 (B) :
What are the rules governing the compensation payable in the event of dishonour of a negotiable instrument under the provisions of The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881?
Answer:
Q 4 (C) :
Ashok and Vimal are pursuing chartered accountancy courses and discussing about the structure of the Indian judicial system. Explain them the functions of the judiciary system of India and the hierarchy of courts and briefly explain their functioning under the Indian Regulatory Framework.
Answer:
Q 5 (A) : (i)
The Institute of Science, Pune (the buyer), placed an order for various chemicals worth ₹1,50,000 from a supplier in Delhi (the seller). The buyer made full advance payment, and the seller dispatched the consignment via a courier of his own choice, without reserving any right of disposal over the goods. The consignment was lost in transit, and now the buyer seeks a refund of the purchase price. With reference to the provisions of The Sale of Goods Act, 1930, assess the validity of the buyer’s claim for a refund.
Answer:
Q 5 (A) : (ii)
Adarsh visited an authorized car showroom and purchased a car of his choice without conducting a detailed inspection. After making the payment and taking delivery of the car, he discovered a defect in the engine that could not have been detected even with a reasonable inspection. With reference to the provisions of The Sale of Goods Act, 1930, advise whether Adarsh can invoke the implied condition of merchantability and repudiate the contract due to the defect in the car.
Answer:
Q 5 (B) : (i)
Explain the following terms under The Indian Partnership Act, 1932:
Answer:
Q 5 (B) : (ii)
"Dissolution of a partnership firm may occur by mutual agreement with the consent of the majority of partners, while compulsory dissolution requires an order from the court." Discuss this statement with reference to the relevant provisions of The Indian Partnership Act, 1932.
Answer:
Q 5 (C) :
Explain with reference to The Indian Contract Act, 1872:
Answer:
Q 6 (A) :
Anjali purchased various cosmetic products worth ₹15,000 during the last week from Sushil, a shopkeeper, on credit of one month. After a fortnight, she makes out a blank promissory note, signed it and delivered to Sushil who further endorsed it to Manish for the payment of his dues. Manish, who is holder in due course, filled up the due amount of ₹17,000 from Sushil and on maturity presented it to Anjali for payment but she refused to pay because the amount filled up is more than the agreed amount of ₹15,000. It is to be noted that the amount of ₹17,000 is covered by the stamp affixed on it. Referring to the provisions of The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 decide, whether Anjali is liable to honour the promissory note to Manish for ₹17,000?
Answer:
Q 6 (A) :
Priya, a small business owner, receives a bill of exchange from her customer, Sanjay, which is due for payment on October 15th. On October 12th, Priya presents the bill of exchange for payment at Sanjay’s office during regular business hours, but Sanjay is not present. Priya leaves the bill with Sanjay’s assistant, requesting it to be presented to Sanjay for payment when he returns. However, Sanjay’s assistant forgot to give the bill, and Sanjay does not make the payment by the due date, and the bill is dishonoured. Based on the provisions of The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, examine whether Priya’s presentation of the bill of exchange to Sanjay’s assistant is valid under law.
Answer:
Q 6 (B) :
What are the conditions to be satisfied for an “Agent’s authority in an emergency” under the provisions of The Indian Contract Act, 1872?
Answer:
OR
Q 6 (B) :
Both a sub-agent and a substituted agent are appointed by the agent, however, there are some points of distinction between the two. Elaborate any 6 points.
Answer:
Q 6 (C) :
What are the rights of a buyer, when seller commits a breach of contract under the provisions of The Sale of Goods Act, 1930?
Answer:
Ruchika Ma'am has been a meritorious student throughout her student life. She is one of those who did not study from exam point of view or out of fear but because of the fact that she JUST LOVED STUDYING. When she says - love what you study, it has a deeper meaning.
She believes - "When you study, you get wise, you obtain knowledge. A knowledge that helps you in real life, in solving problems, finding opportunities. Implement what you study". She has a huge affinity for the Law Subject in particular and always encourages student to - "STUDY FROM THE BARE ACT, MAKE YOUR OWN INTERPRETATIONS". A rare practice that you will find in her video lectures as well.
She specializes in theory subjects - Law and Auditing.
Yash Sir (As students call him fondly) is not a teacher per se. He is a story teller who specializes in simplifying things, connecting the dots and building a story behind everything he teaches. A firm believer of Real Teaching, according to him - "Real Teaching is not teaching standard methods but giving the power to students to develop his own methods".
He cleared his CA Finals in May 2011 and has been into teaching since. He started teaching CA, CS, 11th, 12th, B.Com, M.Com students in an offline mode until 2016 when Konceptca was launched. One of the pioneers in Online Education, he believes in providing a learning experience which is NEAT, SMOOTH and AFFORDABLE.
He specializes in practical subjects – Accounting, Costing, Taxation, Financial Management. With over 12 years of teaching experience (Online as well as Offline), he SURELY KNOWS IT ALL.